Ever exchanged your home currency for another before a trip abroad? If so, you've already participated in the forex market. This guide is your practical introduction to forex trading for beginners, designed to demystify the world's largest financial market and give you the actionable steps to get started with confidence.
Your Friendly Welcome to the World of Forex
It’s easy to feel like financial markets are an exclusive club reserved for experts, but the reality of forex trading is far more straightforward. At its core, you're buying one currency while simultaneously selling another, speculating on which one will strengthen or weaken.
Let’s stick with that travel analogy. Imagine you're flying from the U.S. to Europe. You’d sell your U.S. Dollars (USD) to buy Euros (EUR). If the Euro gains value against the Dollar while you're on vacation, the Euros in your wallet are now worth more Dollars than when you first exchanged them. That, in a nutshell, is the principle behind a profitable forex trade.
Who Is Actually Trading Forex?
The forex market isn't just a playground for giant banks and multinational corporations; it's more accessible than ever. The trading community is surprisingly diverse, especially with younger people jumping in. A recent study found that 27% of forex traders globally are between 18-34 years old.
And if you're worried about being the only newcomer, don't be. A huge chunk of the market—31% of traders, to be exact—have less than one year of experience. You’re in good company! You can get a better sense of who's trading these days by checking out some recent forex statistics.
This open access has made forex a popular path for individuals looking for:
- Financial Growth: The opportunity to profit from correctly predicting currency movements.
- Flexibility: The market runs 24 hours a day, five days a week, so you can trade whenever it fits your schedule.
- A New Skill: Learning to read charts and understand global economic news is a valuable skill in itself.
Our goal here is to give you a rock-solid foundation, building your understanding piece by piece with practical insights from people who have been there. Think of this as your personal roadmap to starting your trading journey on the right foot.
We’re going to walk you through the essential concepts, starting from square one. We'll look at who trades and why, how to "read" the market, and—most importantly—how to manage your risk. Welcome to the world of forex.
Decoding the Language of Forex Trading
Diving into forex for the first time can feel a little like learning a new language. You'll encounter all sorts of technical-sounding terms, but don't let them intimidate you. The core ideas are actually quite simple.
Getting a firm grasp on this vocabulary is the first actionable step toward navigating the market with confidence. Think of it as learning the basic rules of a game—once you know the key terms, you can start to understand the strategy. Let’s break down the essentials you'll encounter every day.
Understanding Currency Pairs
The absolute bedrock of forex trading is the currency pair. You never just buy or sell a single currency in a vacuum; you're always trading one for another. This relationship is shown as a pair, like EUR/USD (the Euro vs. the U.S. Dollar) or USD/JPY (the U.S. Dollar vs. the Japanese Yen).
Every pair has two parts:
- Base Currency: This is the first currency in the pair (the EUR in EUR/USD). It’s the one you're buying or selling.
- Quote Currency: This is the second currency (the USD in EUR/USD). It’s what you're using to make the trade.
So, if you see EUR/USD quoted at 1.0700, it simply means one Euro is worth $1.07. If you buy this pair, you’re speculating that the Euro will get stronger compared to the Dollar. If you sell it, you're betting it will get weaker. For a more detailed look, you can learn more about how to read currency pairs in our guide.
Pips: The Smallest Step
So you understand pairs. How do we measure their price movements? In the forex world, the smallest increment of change is called a pip, which is short for "percentage in point." This is the standard unit traders use to calculate profits and losses.
For most major currency pairs, a pip is the fourth decimal place in the price quote.
For example, if the EUR/USD price shifts from 1.0700 to 1.0701, that's a move of one pip. It might seem incredibly small, but when you’re trading larger volumes of currency, those tiny movements can quickly add up to significant wins or losses.
Leverage: The Seesaw Effect
One of the most powerful concepts you'll encounter is leverage. It's also one of the riskiest, especially for beginners. Leverage is a tool that lets you control a large amount of money in the market using only a small amount of your own capital.
Imagine using a lever to lift a heavy object—a small amount of effort can move a much larger weight. That’s a perfect analogy for leverage: your small amount of capital is used to control a much larger position.
Leverage is a double-edged sword. It can amplify your profits from small price moves, but it can also amplify your losses just as quickly. Learning to use it responsibly is absolutely critical.
A leverage of 100:1, for instance, means that for every $1 you put up from your account, you can control a $100 position. This makes forex accessible to people who don't have millions to invest, but it demands respect.
Market Orders: Your Trading Tools
So how do you actually place a trade? You use orders. These are simply instructions you send to your broker to enter or exit a trade. To start, there are three basic types you need to master.
- Market Order: This is the most direct command. It tells your broker to buy or sell for you immediately at the best available price. Use this when you want to enter the market without delay.
- Limit Order: This lets you set a specific price you're willing to buy or sell at. A buy limit is set below the current market price, and a sell limit is placed above it. Use this when you have a target price in mind and don't want to pay more (or accept less) than that.
- Stop Order (or Stop-Loss): This is your single most important risk management tool. A stop-loss is an order that automatically closes your trade if the market moves against you by a predefined amount, capping your potential losses.
By understanding these fundamentals—currency pairs, pips, leverage, and orders—you've built the foundation. You’re no longer just looking at a screen full of flashing numbers; you’re starting to speak the language of forex.
Getting to Know the Players on the Forex Field
The forex market isn't a physical building; it's a massive, decentralized network of traders, banks, and institutions all buying and selling currencies. Each participant has a different reason for being there, and understanding their motivations is your first step to seeing why currency prices move the way they do.
Think of it as a global ecosystem with large players whose moves can make waves and schools of smaller participants swimming alongside them. It’s not just random numbers blinking on a screen—it's the collective result of millions of decisions. Let's meet the key players.
The Heavyweights: Central Banks and Corporations
At the top tier, you have the institutional giants. These players aren't trying to scalp a few pips on a 5-minute chart; their goals are much bigger, and their actions can shake the entire market.
- Central Banks: These are the key economic players for a country, like the U.S. Federal Reserve (the Fed) or the European Central Bank (ECB). They enter the forex market to manage their country's currency reserves, control inflation, or stabilize their economy. When a central bank makes a move, everyone pays attention because it can cause huge, immediate shifts.
- Multinational Corporations: Companies like Apple or Toyota operate globally, so they are constantly dealing with different currencies. If a Japanese car company sells cars in the U.S., they are paid in dollars but need to pay their factory workers back home in yen. They use forex to convert those dollars to yen, often through a strategy called hedging to protect their profits from adverse currency swings.
These institutions move staggering amounts of money. Their primary goal isn't speculation, but their massive transactions are what create the deep liquidity—the ocean of buyers and sellers—that keeps the entire market running smoothly for everyone else.
The Speculators: From Hedge Funds to Home Traders
Next are the players who are in it purely to profit from currency movements. This group includes everything from billion-dollar hedge funds to individual traders working from home. Their combined activity is what drives most of the day-to-day volatility you see on the charts.
On one end, you have investment funds and professional traders managing huge pools of capital. They make sophisticated bets on currency direction based on exhaustive research and analysis.
And then there's us: the retail traders. We're the individuals, trading our own money through online brokers, looking to capture a piece of the action.
The world of retail trading has grown exponentially. In the United States alone, there are now an estimated 1.3 million forex traders. It's a field dominated by men (91.5%), with the average trader being around 43 years old. If you're curious about the community you're joining, you can dig into more of these numbers by checking out these U.S. forex trading demographics on BestBrokers.com.
For most people, trading starts as a side hustle, but for some, it becomes a full-time profession. Knowing where you fit among these different players helps you make sense of the market's behavior and find your own place in this exciting global arena.
How to Actually Analyze the Forex Market
So, how do you decide when to buy or sell? It's not about gut feelings or flipping a coin. Every sound trading decision stems from a form of analysis. As a beginner, your goal isn’t to master everything at once. Instead, let's get a handle on the two primary methods traders use to find opportunities.
Think of them as two different lenses for viewing the market. One camp studies price charts, looking for patterns. The other camp reads the news and analyzes economic reports. Most seasoned traders end up using a blend of both, but it’s much easier to learn them one at a time.
Let’s break them down.
Technical Analysis: Reading the Market's Story
Technical analysis is the practice of looking at charts to predict what might happen next. Think of it like being a weather forecaster. A meteorologist studies historical weather patterns—what happened the last time a cold front from the north met warm, humid air—to make an educated forecast about tomorrow's weather.
That’s essentially what a technical analyst does. They operate on the belief that everything you need to know—all the news, economic data, and general market sentiment—is already reflected in the price on the chart. Their goal is to spot recognizable patterns and trends that hint at where the price might be headed.
For instance, one of the first concepts you should learn is support and resistance.
- Support: This is a price level where a currency pair tends to stop falling. Imagine it as a floor that the price has a hard time breaking through. It suggests buyers are stepping in.
- Resistance: This is the opposite—a price level where a currency pair struggles to climb higher. Think of it as a ceiling. It suggests sellers are taking control.
By identifying these "floors" and "ceilings" on a chart, a technical trader can plan their moves, such as buying near a support level or selling near resistance. It’s about using the chart's own history to create a story about its potential future.
Fundamental Analysis: Connecting News to Price
While technical traders focus on their charts, fundamental analysis involves zooming out to look at the bigger picture. This approach is all about determining a currency's intrinsic value based on the economic, social, and political health of its home country. It’s less about patterns and more about real-world cause and effect.
Think of yourself as a detective investigating a country's economy. You’d be asking questions like:
- Is the economy growing? Check the latest GDP reports.
- Are interest rates going up or down? Watch for central bank announcements.
- How many people are unemployed? That's what unemployment data reveals.
- Is the government stable? Pay attention to elections and major policy shifts.
A strong, growing economy with rising interest rates tends to attract foreign investment, which usually makes its currency stronger. For example, if the U.S. Federal Reserve unexpectedly raises interest rates, the U.S. Dollar (USD) often strengthens against other currencies. A fundamental trader would have either anticipated this or acted quickly on the news.
At its heart, fundamental analysis is built on the idea that a currency's exchange rate will eventually align with the true health of its economy. It helps you understand the "why" behind major market swings.
To help you see the differences more clearly, here's a quick side-by-side comparison.
Technical vs Fundamental Analysis At a Glance
| Aspect | Technical Analysis | Fundamental Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Tools | Price charts, indicators, patterns | Economic data, news reports, political events |
| Core Question | "What is the price doing?" | "Why is the price doing what it's doing?" |
| Timeframe | Short-term to medium-term | Medium-term to long-term |
| Key Assumption | Market history repeats itself. | A currency's value reflects its economic health. |
| Example | Buying a currency pair when it bounces off a known support level. | Selling a currency after its country reports weak employment numbers. |
Ultimately, both approaches are tools designed to give you an edge. Neither one is inherently "better"—it's all about what resonates with your personality and trading style.
Finding an approach that feels right is a huge part of your journey as a trader. For a deeper look at the specific methods and tools involved, check out our guide on the best forex market analysis techniques.
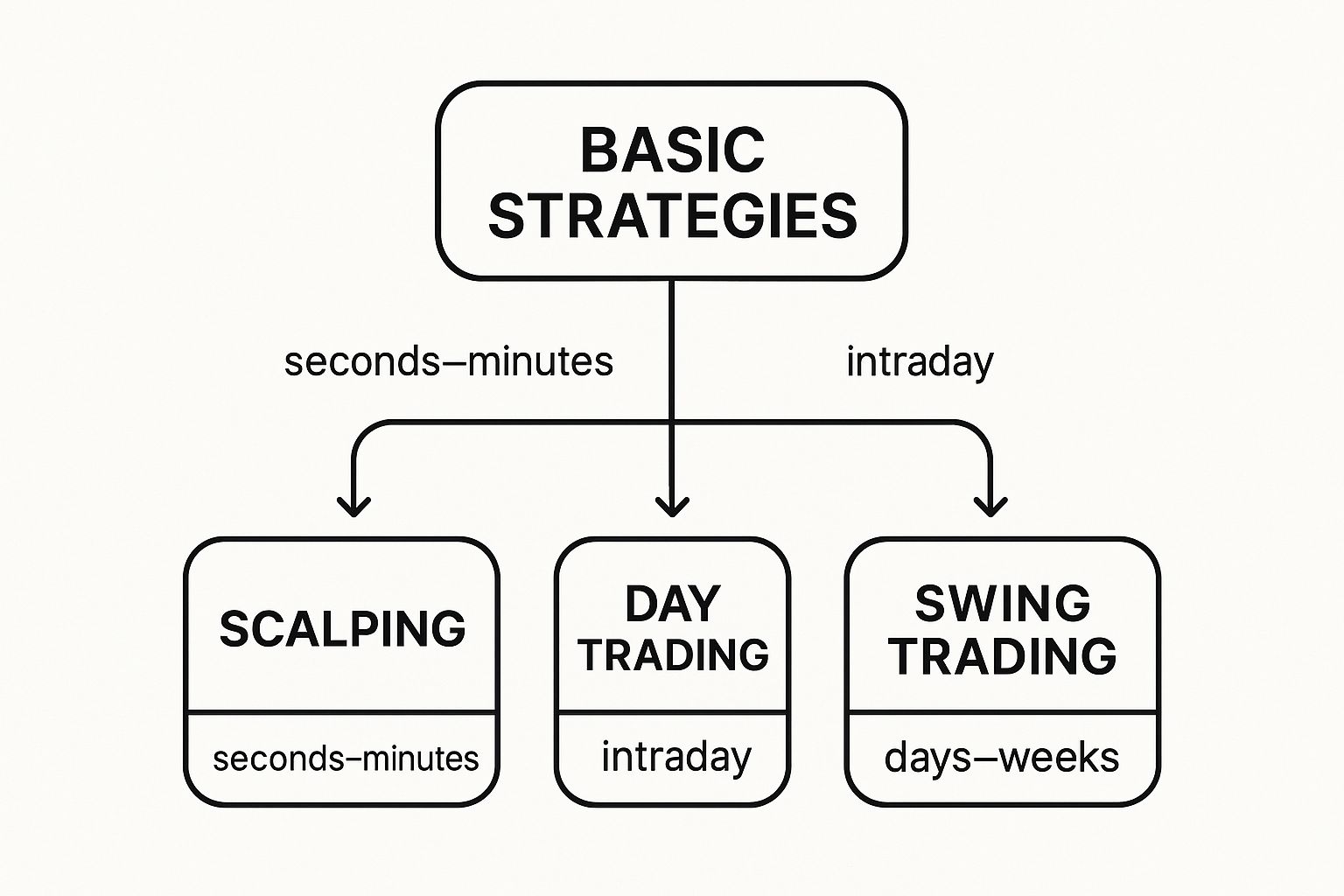
This image below helps illustrate how different analysis styles often align with different trading strategies, which are largely defined by how long a trade is held open.
As you can see, very short-term strategies like scalping and day trading rely heavily on technicals. Longer-term approaches like swing or position trading almost always incorporate fundamentals into the mix.
In the end, many traders start with one and slowly add elements of the other as they gain experience. The best method for you is the one you understand, trust, and can apply consistently.
Smart Risk Management for New Traders
If you take only one lesson away from this guide, let it be this one. The key to longevity as a forex trader isn't hitting a few spectacular wins. It's about systematically managing the inevitable losses so you can protect your capital and stay in the game.
Think of your trading capital as the lifeblood of your operation. Once it's gone, you're out. So, let's talk about actionable strategies you can implement right now to safeguard that capital and trade like a professional from day one.
The Power of the One Percent Rule
One of the most effective—and refreshingly simple—risk management techniques is the 1% Rule. The concept is straightforward: never risk more than 1% of your total trading capital on a single trade. This one simple rule is your best defense against blowing up your account after a few bad trades.
Here’s how it works in practice:
- Let's say you have a $5,000 trading account.
- With the 1% Rule, the absolute maximum you can afford to lose on any one trade is $50 (which is 1% of $5,000).
This doesn't mean you can only trade tiny amounts. It means you structure your trade so that if it goes completely wrong and hits your maximum loss point, the damage is capped at a manageable $50. A loss like that stings, but it won't knock you out. You can learn from it and move on to the next opportunity with a clear head.
Sticking to the 1% Rule shifts your mindset from gambling to running a business. It ensures that a string of losses—which happens to every single trader—doesn't end your career before it even begins.
Your Automated Safety Nets
How do you actually enforce the 1% Rule without hovering over your screen 24/7? You use your broker's built-in tools. Think of these as your automated, non-negotiable safety nets.
-
Stop-Loss Order: This is your best friend in trading. Before you even enter a position, you place an order telling your broker to automatically close the trade if the price moves against you to a certain level. This is how you define your 1% risk and ensure your loss never spirals out of control.
-
Take-Profit Order: This is the other side of the coin. It’s an order to automatically close your trade once it hits a predetermined profit target. This is crucial for locking in your wins and fighting the greed that makes traders hold on too long, only to watch a winning position turn into a loser.
These tools are powerful because they take emotion out of the equation right when you're most vulnerable. They execute the plan you made when you were calm and rational, no matter how tempted you are to bend the rules in the heat of the moment.
Taming Your Trading Psychology
Even with the best strategies and tools, your biggest adversary will often be your own emotions. The high of a win and the sting of a loss can lead to destructive habits. When real money is on the line, those emotions are amplified. For instance, the average deposit for Australian forex accounts was $8,400 back in 2021, showing that people often start with significant capital at risk. You can dig into more stats like this in a great forex trading report.
One of the most common rookie mistakes is revenge trading—that impulsive urge to jump straight back into the market after a loss to try and "win it back." This is a recipe for disaster because you're trading based on emotion, not a sound strategy.
Your best defense is a written trading plan. This document is your personal rulebook. It lays out the exact conditions for entering a trade, where you’ll set your stop-loss and take-profit, and how you’ll manage risk. It’s the professional anchor that keeps you grounded when emotions run high.
Your First Actionable Steps into the Market
Alright, let's roll up our sleeves and discuss how you actually get started. Theory is one thing, but making your first moves in the forex market is where the rubber meets the road. This is your practical, step-by-step guide to doing it the right way.
We're going to cover finding a broker, practicing without risking a penny, and putting together a basic game plan.
Think of it like learning to drive. You wouldn't just hop onto the freeway. You'd find a good instructor, practice in an empty parking lot, and have a clear destination in mind. Trading requires that same deliberate preparation.
Finding a Trustworthy Broker
Your broker is your gateway to the forex market. They provide the software you trade on, execute your orders, and hold your funds, so choosing the right one is a critical decision. It can feel like a crowded space, but you can filter out the noise by focusing on what truly matters.
Here’s your checklist of non-negotiables:
- Strong Regulation: Is the broker overseen by a top-tier financial authority? Look for names like the FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), or CySEC (Europe). This is your number one safeguard.
- An Intuitive Platform: As a newcomer, you need software that's easy to use. Platforms like MetaTrader 4, its successor MetaTrader 5, or cTrader are popular because they are powerful yet fairly intuitive.
- Low Spreads and Fees: The spread is the small difference between the buy and sell price—it's how brokers get paid. The tighter the spread, the lower your trading costs, which directly impacts your potential profit.
- Reliable Customer Support: You will have questions. Make sure you can reach a real, helpful person when you need them.
Practice with a Demo Account
Once you have a couple of brokers in mind, it's time for the single most important step for any new trader: open a demo account. This is your trading simulator. It lets you trade with virtual money in the live market, so you can experience everything without risking any of your own capital.
A demo account is where you build skills and confidence. It’s the perfect, stress-free environment to test strategies, learn the platform, make your rookie mistakes, and find your footing.
Use this time to get comfortable placing orders, setting your stop-loss and take-profit levels, and simply observing how the market moves. Do not even consider putting real money on the line until you can consistently achieve the results you want in your demo account.
Your First Steps Checklist
To make this crystal clear, here’s a simple checklist to get you started. Ticking off these boxes will help you begin with a strong, sensible foundation.
| Step | Action Item | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Choose a Broker | Select a regulated broker with a user-friendly platform. | Is it regulated by a major authority? Are the spreads competitive? |
| 2. Open a Demo Account | Sign up for a free practice account with your chosen broker. | Can you practice your strategy effectively with the tools provided? |
| 3. Create a Simple Plan | Write down basic rules for your trading. | Define what currency pairs you will trade and your risk per trade (e.g., 1% rule). |
| 4. Practice Consistently | Trade on your demo account as if it were real money. | Track your results to identify what’s working and what isn’t. |
Following these steps isn't just about going through the motions; it's about building the discipline and habits that separate successful traders from those who burn out. Take your time, be patient, and focus on mastering the process.
Common Questions from New Forex Traders
It’s completely normal to have a lot of questions when you first explore forex trading. In fact, asking questions is a great sign—it means you're taking this seriously.
Let's wrap up by tackling some of the most common things beginners ask. Think of this as a final Q&A to clear up any lingering confusion before you get started.
How Much Money Do I Really Need to Start?
This is the big one. The short answer is, it varies. Thanks to leverage, some brokers allow you to open an account with as little as $100. However—and this is a big however—starting that small makes proper risk management almost impossible.
A more realistic starting point for most new traders is between $500 and $1,000. This amount of capital is enough to let you properly apply risk management principles—like the 1% rule we discussed—without having your potential profits erased by spreads.
Here’s the golden rule: Only trade with money you can comfortably afford to lose. This is your "risk capital." Never fund a trading account with money you need for rent, groceries, or other essential expenses.
Is Forex Trading Just Gambling?
That's a fair question, and it gets to the heart of what separates a disciplined trader from a reckless one. Trading becomes gambling when you enter the market without a plan, ignore risk limits, and make decisions based on pure emotion.
But that's not what professional trading is about. Strategic forex trading is about managing probabilities. It's built on a foundation of:
- A Solid Strategy: Using analysis to find setups with a high probability of success.
- Strict Risk Management: Knowing exactly how much you stand to lose on a trade before you enter.
- Emotional Discipline: Having the fortitude to follow your plan, even when fear or greed is tempting you to deviate.
No single trade is a guaranteed win. A smart trader focuses on putting the odds in their favor over a long series of trades. A gambler just closes their eyes and hopes for a lucky break.
What Are the Best Currency Pairs for Beginners?
When you’re just starting out, simplicity is key. Your best bet is to stick with the major currency pairs. These are the most heavily traded pairs on the world stage, typically pairing the U.S. Dollar with currencies from other major economies.
Pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY are ideal for beginners. Why? Because they have immense trading volume, which means there are always plenty of buyers and sellers. This generally results in tighter spreads (lower costs for you) and more predictable price action compared to the wilder, more exotic pairs.
Focus on learning the behavior of one or two of these majors first. It's the best way to understand the rhythm of the market without getting overwhelmed.
Ready to put what you've learned into practice without risking a single dollar? Agfin Ltd created Finance Illustrated as a free resource hub designed specifically for new traders. You can check out our easy-to-digest Forex course, play around with trading simulators, and build your confidence before ever going live. Start your journey today at https://financeillustrated.com.