Think of diversifying your investment portfolio like building a playlist. You wouldn't just put one song on repeat, right? You mix different artists and genres. Investing is the same: instead of betting all your money on a single stock, you spread it across different types of investments. It’s a key strategy that helps protect your money if one investment has a bad day, making your financial journey a lot smoother.
Why Diversification Is Your Best Friend in Investing
Let’s imagine you put all your savings into one hot tech stock. It feels amazing when it’s soaring, but what happens when a new competitor shows up or they have a bad quarter? History is full of superstar companies that faded away, like Blockbuster or Myspace. Going all-in on one company is a huge gamble.
Here’s a wild fact: during the 2022 market downturn, a massive 96% of individual stocks in the S&P 500 dropped in value. That’s a tough stat if you only own a couple of them.
This is where diversification comes in to save the day. It’s a concept that the mega-successful investor Warren Buffett explained perfectly:
"Never put all your eggs in one basket."
This isn't just an old saying; it’s the secret sauce of smart investing. By owning a mix of different assets, you create a team where each player has a different strength. When one part of your portfolio is down, another part might be doing just fine, or even great. It’s like being a chef: you don’t make an amazing dish with just one ingredient. You blend different flavors to create something awesome.
Getting a Feel for the Landscape
The investment world is always changing. Last year's MVP could be this year's benchwarmer. In fact, one study that tracked different investments for 20 years found that the "best" one – whether it was international stocks, real estate, or just cash – changed almost every single year.
That unpredictability is exactly why having a smart mix is so important. The first step is to get to know the key players on the field.
A Quick Look at Investment Types and Risk
To get started, it helps to know the main types of investments, or "asset classes," and how risky they generally are. Think of this as your investor starter pack.
| Asset Class | What It Is (In Simple Terms) | Typical Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Stocks (Equities) | Owning a small piece of a company. | High |
| Bonds | Loaning money to a government or company. | Low to Medium |
| Real Estate | Investing in physical property. | Medium |
| Commodities | Raw materials like gold, oil, or even coffee. | High |
| Cash & Equivalents | Money in savings accounts or short-term bonds. | Very Low |
Getting familiar with these basic building blocks is the first real step toward building a portfolio that can handle the market's ups and downs.
Building Your Core Investment Mix
Alright, let's get to the fun part: building your investment team. You can't just have all star quarterbacks; you need great defenders and all-rounders, too. Each one has a job to do.
In investing, these "players" are called asset classes. It’s just a fancy way of grouping different types of investments.
The two main players everyone knows are stocks and bonds. Stocks are your star attackers – they have the potential for big growth, but they also come with more risk. When you buy a stock, you're buying a tiny piece of a company like Apple or Nike. Some even pay you a slice of their profits, called dividends. If you're curious, checking out a list of the best dividend stocks to buy can give you a feel for how they work.
Bonds, on the other hand, are your reliable defense. You're basically loaning money to a government or a big company, and they pay you back with interest. They're usually much more stable than stocks, acting as an anchor when the market gets choppy.
Expanding Your Roster Beyond the Basics
A great team needs more than just offense and defense. To build a truly diversified portfolio that can handle anything, you need to bring in some other key players.
Of course, before adding any new asset, it's essential to understand how to calculate return on investment. This is a must-have skill that lets you compare different opportunities fairly.
Here are a few other asset classes to consider for your lineup:
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Ever wanted to invest in real estate but don't want the hassle of being a landlord? REITs are for you. These are companies that own buildings that make money – think apartment complexes, shopping malls, or office towers. You get to collect a piece of the rent without fixing a single leaky faucet.
- Commodities: We're talking about raw materials here – stuff like gold, silver, and oil. Gold is a classic "safe-haven" asset. When the stock market gets scary and people start selling, the price of gold often goes up, providing a nice balance.
- Cash Equivalents: This is your emergency fund inside your portfolio. Think high-yield savings accounts or super safe, short-term government bonds. It’s the safest part of your portfolio, earning a little interest while waiting for a great investment opportunity to pop up.
Why This Mix Matters
So, why go to all this trouble? Because these different assets rarely move up and down at the same time.
It’s all about creating balance. In a year when your stocks might be struggling, your bonds or gold could be doing well, helping to soften the blow to your overall portfolio. This blend smooths out the wild rides, which is key to staying invested for the long run.
Billionaire investor Ray Dalio famously called this the "Holy Grail of investing."
"The Holy Grail of investing is to have a portfolio of 15 or more uncorrelated assets."
Now, you don't need to run out and find 15 different things to invest in tomorrow. The main idea is what’s important. By spreading your money across different players – stocks for growth, bonds for stability, and others like REITs or commodities for special roles – you’re building a tough portfolio that’s ready for any economic season.
Investing Beyond Your Own Backyard
Only investing in your home country is like only listening to artists from your hometown. Sure, you know them and they're great, but you’re missing out on a whole world of amazing music. The same goes for your money. This is where geographic diversification comes in – it’s your passport to finding growth all over the globe.
Every country's economy moves at its own pace. When the U.S. market is slow, another market somewhere else could be booming. By spreading your investments across different countries, you're not just playing defense; you're setting yourself up to catch growth wherever it's happening.
Why Look Abroad?
It's tempting to stick with what you know, but there's a huge world of opportunity out there. Pushing your portfolio beyond your country's borders is a proven strategy for building a stronger, long-term portfolio.
Here’s why it's a smart move:
- Different Economic Cycles: Economies rarely move in perfect sync. A slow year at home might be balanced by a great year in a developed market like Germany or a fast-growing emerging market like India.
- Access to Global Giants: Many of the world's coolest companies aren't American. Think of industry leaders like Samsung (South Korea), luxury brand LVMH (France), or even TikTok's parent company ByteDance (China). Investing internationally gives you a piece of their success.
- Currency Magic: Changes in currency exchange rates can actually help you. A strong dollar might make foreign stocks cheaper to buy, while a weaker dollar can boost the value of your international profits when you bring them back home.
We saw this in action back in 2025, when portfolios with global investments did better than those that just stuck to the U.S. Why? A big reason was that stocks in places like Europe and Japan were a better deal and got a nice boost from currency trends.
Putting It Into Practice
The good news is you don't need a Swiss bank account to invest internationally. For most people, the easiest way is through funds that do all the work for you.
- International ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds): These are like baskets of stocks that track indexes from different countries or regions. You can easily buy an ETF that covers developed markets (like Europe and Japan) or one that focuses on emerging economies (like Brazil and India).
- Global Mutual Funds: These funds are run by pros who pick and choose stocks from all over the world, trying to find the best opportunities to grow your money.
And don't forget about physical assets. When you're diversifying with real estate, learning about powerful tax-deferred investment strategies like the 1031 exchange can make a huge difference to your final profits.
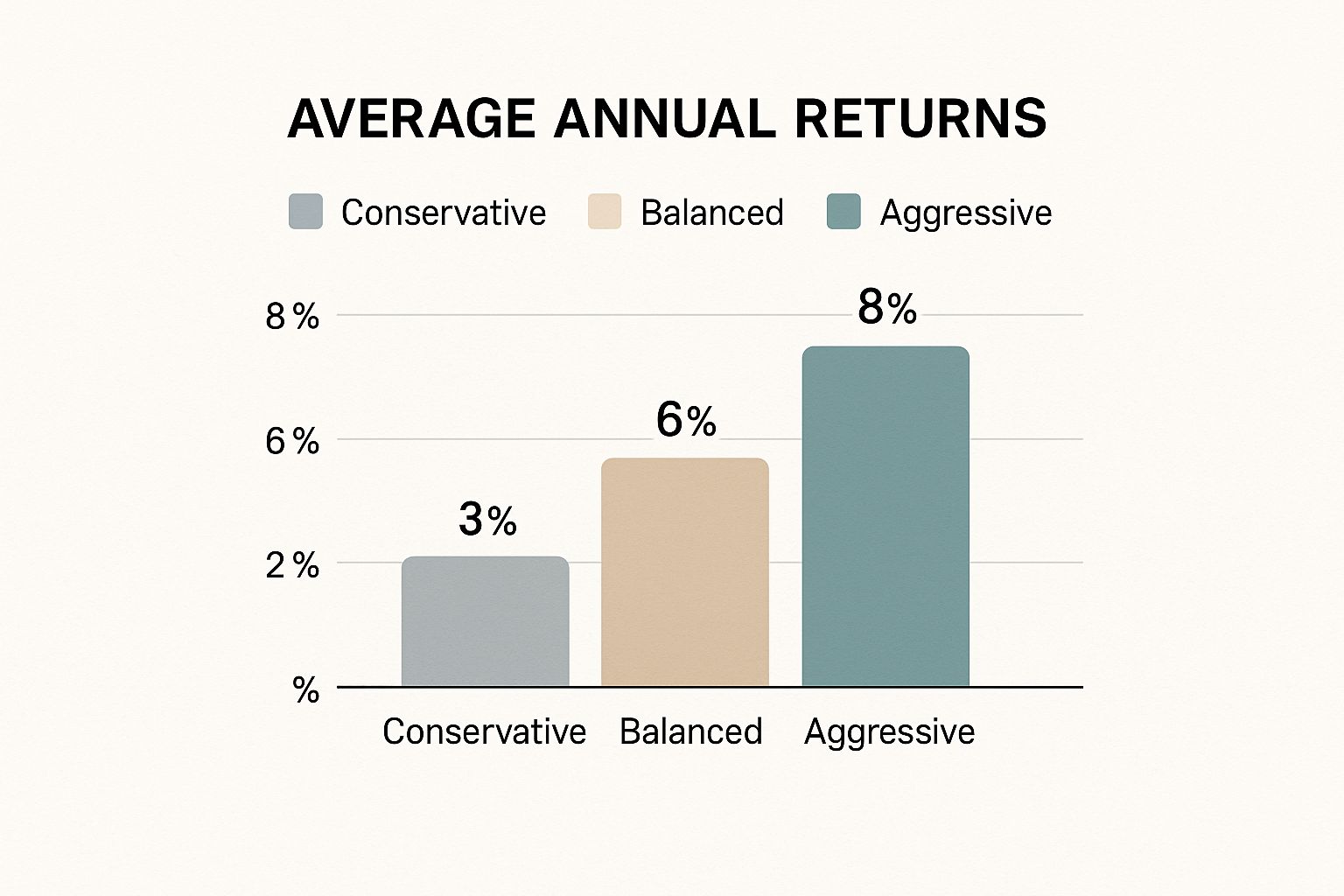
This chart shows how different investment strategies, including those with global stocks, can really affect your average annual returns over time.
As you can see, the strategies that usually make more money often have a healthy amount of growth-focused investments – and international stocks are a key ingredient in that mix.
US Stocks vs International Stocks A Snapshot
It's not about choosing one over the other; it's about seeing how they work together. This quick comparison shows why having both U.S. and international stocks in your portfolio is a power move.
| Factor | U.S. Market Focus | International Market Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Sources | Driven by U.S. shoppers, tech, and government decisions. | Taps into different economies, growing middle classes, and global trade. |
| Major Companies | Access to giants like Apple, Amazon, and Microsoft. | Exposure to leaders like Toyota, Samsung, and Nestlé. |
| Currency Risk | None (your investments are in USD). | Affected by currency changes, which can be both a risk and an opportunity. |
| Economic Exposure | Focused on the ups and downs of the U.S. economy. | Spreads risk across many economies, so you're not dependent on just one. |
Ultimately, combining both gives you a more balanced and strong portfolio, helping you smooth out the ride and capture growth no matter where in the world it’s happening.
Finding Your Personal Risk Comfort Zone
Before you start picking investments, you need to have an honest chat with yourself. The big question is: how much risk can you handle without freaking out? This is your risk tolerance, and it’s totally personal.
Figuring this out is less about math and more about knowing yourself. Are you a thrill-seeker who loves a roller coaster, or do you prefer a chill, predictable boat ride? There's no right or wrong answer. It's about building a portfolio that fits your personality.
What's Your Investing Style?
Your age and how long you plan to invest are probably the biggest clues to your risk level.
If you’re young, you have an incredible superpower: time. With decades ahead of you, you can afford to ride out the market’s ups and downs. A portfolio with a lot of stocks makes sense because the long-term growth potential is huge.
But if you're close to retirement, the game totally changes. Your main goal switches from growing your money to protecting what you’ve built. This is where the stability of bonds and other safer assets becomes your best friend.
"The individual investor should act consistently as an investor and not as a speculator." – Benjamin Graham
This piece of wisdom from the legendary investor Benjamin Graham is perfect. Your strategy shouldn't be about chasing quick wins; it should be a plan that lets you sleep at night.
To figure out your style, think about these three things:
- Your Timeline: When will you need this money? A longer timeline usually means you can take on more risk.
- Your Goals: Saving for a car in two years needs a much safer plan than saving for retirement in 40 years.
- Your Gut Reaction: Seriously, imagine your portfolio value dropped by 20% in a month. If your first instinct is to panic and sell everything, you’re probably better off with a more careful strategy.
What Different Risk Profiles Look Like
So, what does this look like in real life? Let’s say you have $10,000 to invest. Here’s a simple breakdown of how you might split it up based on different comfort levels.
| Portfolio Type | Stock Allocation (Growth) | Bond Allocation (Stability) | Real Estate/Alternatives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggressive | 70% ($7,000) | 20% ($2,000) | 10% ($1,000) |
| Moderate | 50% ($5,000) | 40% ($4,000) | 10% ($1,000) |
| Conservative | 30% ($3,000) | 60% ($6,000) | 10% ($1,000) |
As you can see, the aggressive portfolio is all about growth, making it a great fit for someone young with a long career ahead of them, like the 27-year-old Zendaya.
On the other hand, the conservative mix focuses heavily on stability. This approach would be much better for someone like Harrison Ford, whose main goal now is to protect his wealth.
Your goal is to find your sweet spot – a diversification strategy that helps you reach your financial goals and feels right for you.
How to Keep Your Portfolio on Track
So, you’ve done the hard work and built your perfect investment mix. Let's say you chose a classic 60% stock and 40% bond split. Right now, it’s perfectly balanced for your goals and risk level.
But here’s the thing: your portfolio doesn't sit still.
Imagine your stocks have an amazing year and their value shoots up. That perfect 60/40 balance is suddenly more like 70/30. Without you doing anything, your portfolio has become riskier than you planned. This sneaky change is called portfolio drift.
The fix? It’s a simple but super important habit called rebalancing. This is just the process of hitting the reset button every so often to get your investments back to their original percentages. Think of it like a regular tune-up for your car – it keeps everything running smoothly and safely.
The Art of Buying Low and Selling High
Rebalancing might sound technical, but its logic is simple and smart. It automatically makes you follow the oldest rule in investing: buy low and sell high.
When you rebalance, you’re selling a bit of what has done well (selling high) and using that money to buy more of the assets that have fallen behind (buying low). It’s a disciplined strategy that removes emotion from your decisions. You aren't trying to guess what the market will do next; you're just sticking to your original plan.
"The stock market is a device for transferring money from the impatient to the patient." – Warren Buffett
Buffett's famous line is all about rebalancing. It’s a patient, disciplined approach that stops you from chasing hot stocks or panic-selling when things dip. It’s all about steady maintenance.
How Often Should You Rebalance?
Now, this doesn't mean you need to check your account every day. Not at all. For most investors, one of these two simple methods works perfectly:
- Time-Based Rebalancing: This is the "set it and forget it" approach. Just pick a schedule – once a year, every six months, or every quarter – and make your adjustments then. For many people, once a year is perfect.
- Threshold-Based Rebalancing: This method is a bit more hands-on. You set a specific trigger, say 5%. If any part of your portfolio drifts more than 5% from its target (like your 60% stock portion grows to 65%), that’s your signal to rebalance.
Sticking to a rebalancing plan is what really protects your portfolio. The data proves it. In 2022, the S&P 500 fell a painful 18.11%. But, historical analysis from firms like Envestnet shows that a well-diversified and regularly rebalanced portfolio could have softened that blow, limiting losses to around 11.80%. It’s a powerful reminder of how important this simple tune-up can be.
Once you have a strategy, it's a good idea to see how it might have done in the past. To learn more, check out our guide on how to backtest trading strategies. It can give you a better feel for how your chosen mix might act in different markets.
The Evolving World of Alternative Investments
We've covered the big players: stocks, bonds, and real estate. They’re the foundation of most solid investment plans. But what if you could invest in things that move to their own beat, often not caring what the stock market is doing?
Welcome to the fascinating world of alternative investments.
Think of these as the indie bands of the investment world. They don't always follow the mainstream charts. This huge category includes everything from fine art and rare sneakers to shares in private companies and even crypto like Bitcoin.
For a long time, this was a world only for the super-rich. You’d hear stories of billionaires like Steve Cohen building art collections worth over $1 billion, treating it as a serious financial asset. Meanwhile, the average person was stuck on the outside.
Making Alternatives Accessible
Thankfully, that’s all changed. A whole new wave of platforms has popped up, letting everyday investors buy a tiny piece of a famous painting, invest in a cool startup before it goes public, or add a slice of a private credit fund to their portfolio.
This isn’t about going all-in on crypto or trying to flip collectibles for a quick profit. It’s about strategically putting a small part of your portfolio – say, 5% to 10% – into assets that are uncorrelated with traditional markets. Simply put, when your stocks go down, these assets might go up, adding another layer of stability to your financial life.
"The key is to find things that have a low correlation so that you get the risk-reducing benefits of diversification." – Ray Dalio
Hedge fund legend Ray Dalio said it perfectly. The goal isn't just to add more stuff to your portfolio; it's to add different types of risk and potential reward.
A Modern Approach to Diversification
This shift hasn't been missed by the big investment firms. Major companies now see that alternatives like hedge funds, real assets, and even digital currencies are becoming essential tools for building strong portfolios. As BlackRock's latest investment insights point out, these assets are used to lower the risk of having all your eggs in one basket.
So, what are some of these cool, accessible alternatives? Here are a few to get you thinking:
- Crowdfunded Real Estate: Instead of buying a whole property, you can invest in specific projects with other people.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending: You become the bank, lending money directly to people or small businesses for a set return.
- Collectibles: New platforms let you buy shares in everything from rare comic books and classic cars to cases of fancy wine.
Dipping your toes into alternatives is a powerful way to learn how to diversify your investment portfolio for the modern world. By thinking beyond the classic stock-and-bond box, you can build a stronger, more resilient portfolio that’s ready for whatever the future holds.
Got a Few Lingering Questions About Diversification?
Even with a solid plan, it's normal to have a few questions. Let's clear up some of the most common ones I hear from new investors.
First off, people always ask, "How much money do I actually need to diversify?" The good news is, you don't need a huge pile of cash. Thanks to things like ETFs and fractional shares, you can own a piece of hundreds of companies with as little as $5. Seriously.
So, Can You Be Too Diversified?
Believe it or not, yes. There's a point where it stops helping, sometimes called "diworsification."
When you spread your money across too many different things – we're talking hundreds of stocks and funds – your portfolio starts to look like a watered-down version of the whole market. The great performance of your big winners gets canceled out by everything else, and just keeping track of it all becomes a nightmare.
The legendary investor Peter Lynch had a great take on this: “Owning stocks is like having children – don’t get involved with more than you can handle.”
For most of us, a well-built portfolio with around 10 to 15 different assets – like a few core ETFs mixed with some individual stocks or bonds you really believe in – is more than enough to get the job done.
Can You Diversify Within a Single Asset Class?
Totally. In fact, this is a smart move that adds another layer of safety.
Let's say you're excited about the tech industry. Instead of putting all your money into one company, you could spread it across different types of tech businesses.
- The Giants: Think established players like Apple or Microsoft.
- The High-Flyers: Look at faster-growing software or cybersecurity companies.
- The "Picks and Shovels": Consider the companies that make the essential parts, like computer chips.
This same idea works for bonds and real estate, too. By owning different types of assets within the same category, you protect yourself if one specific corner of that market has a bad year. One bad apple won't spoil the whole bunch.
Here at financeillustrated.com, our goal is to make complex financial ideas simple and something you can actually use. If you’re ready to start building a stronger financial future, check out our free Trading School and try out our simulators to practice without any risk.