Jumping into the stock market is a lot simpler than most people think. Seriously. To get started, you just need to open a special account, put some money in it, and pick your first investment – whether that’s a single stock or a bundle of them called an ETF.
Buying your first share is literally as easy as tapping a button on an app, and you can often get going with just $5 or $10.
Your Guide to Stock Market Investing
Ready to finally get your money working for you? When you buy a stock, you're owning a tiny piece of a company you probably already use, like Nike or Netflix. If the company does well, the value of your piece can grow with it.
First, let's bust a huge myth: you don't need a pile of cash to start. In fact, one little-known fact is that many of America's first millionaires were school teachers who started small and invested consistently over their careers. It's all about starting early and letting your money grow.
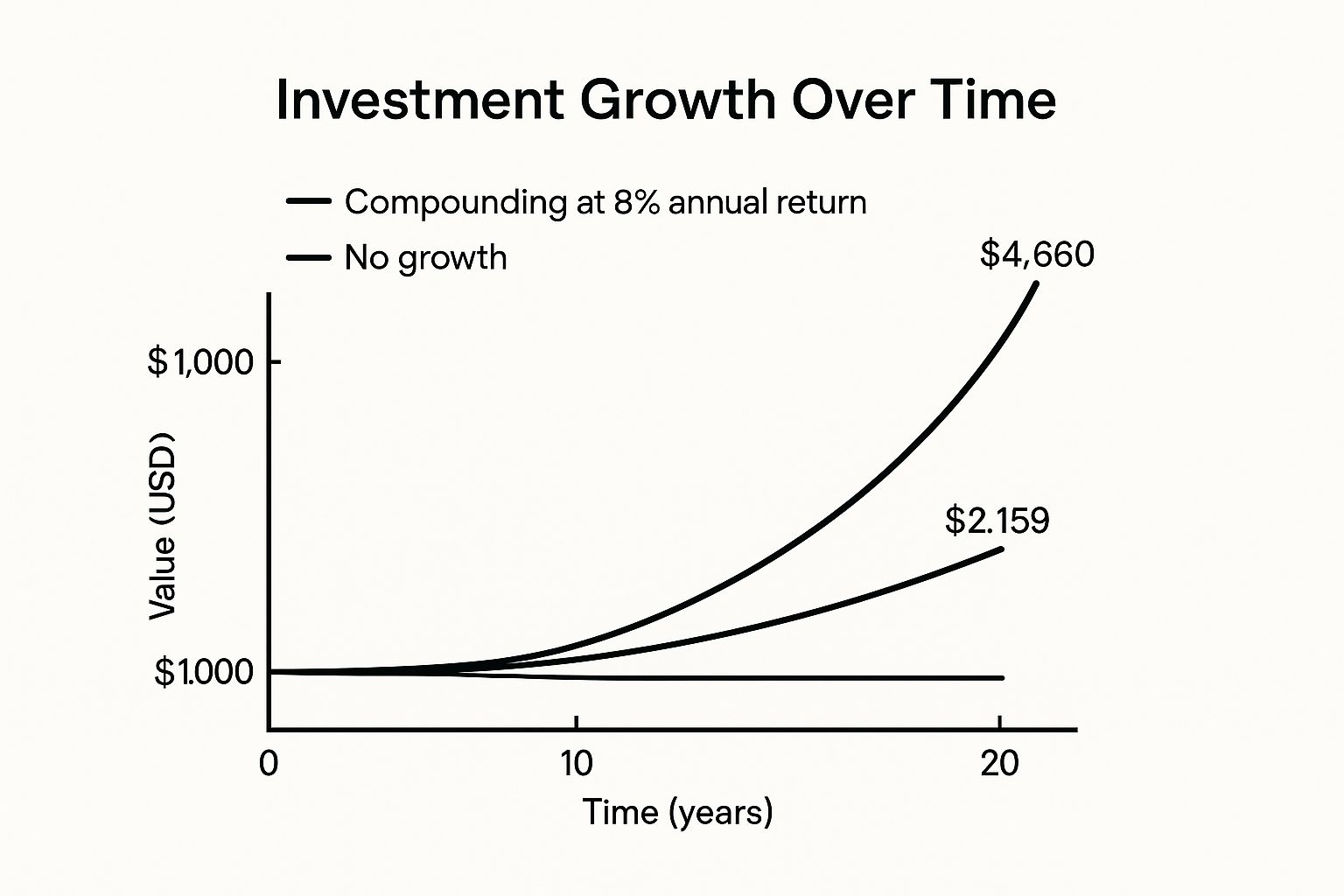
"Compound interest is the eighth wonder of the world. He who understands it, earns it; he who doesn't, pays it." – Often attributed to Albert Einstein
That quote is the secret sauce. Compounding is when your earnings start making their own earnings. It's like a small snowball rolling downhill, getting bigger and faster as it picks up more snow. Even a small start can turn into something huge over time.
Your Investing Quick Start Roadmap
Think of this guide as your roadmap. We'll walk through everything you need to know, making this feel less like a boring finance class and more like a smart, practical adventure.
Here’s a bird’s-eye view of the journey ahead.
| Phase | What You Do | The Big Picture |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Open and fund a brokerage account. | This is your home base for all your investments. |
| Selection | Pick your first stocks or ETFs. | You're choosing which companies you want to own a piece of. |
| Execution | Place your first buy order. | This is the exciting moment you officially become an investor. |
| Growth | Develop long-term habits. | You'll learn how to manage and grow your money over time. |
By following these phases, you'll build the confidence to not just start investing, but to stick with it. This isn't about getting rich overnight; it's about making smart, steady decisions that build a strong foundation for your financial future.
Choosing the Right Brokerage Account
Before you can buy that first piece of a company, you need a place to do the buying and selling. That's a brokerage account. Think of it as a special bank account just for your investments.
Getting this first step right makes everything else so much smoother. Your choice of broker isn't a minor detail; it's your first real investing decision and the main tool you'll use to build wealth.
Find the Account That Fits You
For most beginners, the choice is between a standard brokerage account or a Roth IRA. A standard account offers the most flexibility, but a Roth IRA is a secret weapon for retirement, letting your money grow completely tax-free.
The potential here is huge. The entire global stock market is worth over $100 trillion. An interesting fact is that if you had invested just $100 in the S&P 500 (a mix of the 500 biggest US companies) back in 1980, it would be worth over $10,000 today. Modern brokerage apps have made it super easy for anyone to get a piece of that action.
Basketball legend Shaquille O'Neal said it best: "It is not about how much money you make. The question is are you educated enough to KEEP it." Choosing the right account is the first step to keeping – and growing – more of your hard-earned money.
What to Look For in a Broker
When you’re looking for a broker, it's easy to get overwhelmed. Just focus on a few key things that really matter for new investors. You'll want a platform that’s easy to use, offers good learning tools, and – most importantly – has low fees. Hidden costs are the silent killers of your future earnings.
Here’s a quick checklist of must-haves:
- Low Fees: This is a big one. Many top brokers now offer $0 commission on stock trades. Don't settle for less.
- A Great App: If the app is clunky or confusing, you're not going to use it. Find one that feels natural to you.
- Learning Resources: The best brokers want you to succeed. They provide articles, videos, and tutorials to help you learn as you go.
Some platforms are for hyperactive day traders, while others are perfect for a more relaxed "set it and forget it" style. Don't be afraid to poke around and see which one feels right. For a much deeper dive into the costs, check out our guide on comparing brokerage fees to see how the top players stack up.
How to Pick Your First Investments
Alright, this is where the fun really begins – deciding where to put your money. With thousands of companies out there, it can feel paralyzing. So, let's cut through the noise and keep it simple.
A great starting point is to invest in what you know and use every day. Seriously, look around you. Are you reading this on an iPhone? Apple (AAPL) is a stock. Did you watch a movie last night? Netflix (NFLX) is a stock. Love your sneakers? Nike (NKE) is a stock.
This isn’t just a cute trick; it’s a strategy that legendary investors use. When you're a customer, you have a natural advantage. You understand the products and can often tell when a company is doing great or falling behind.
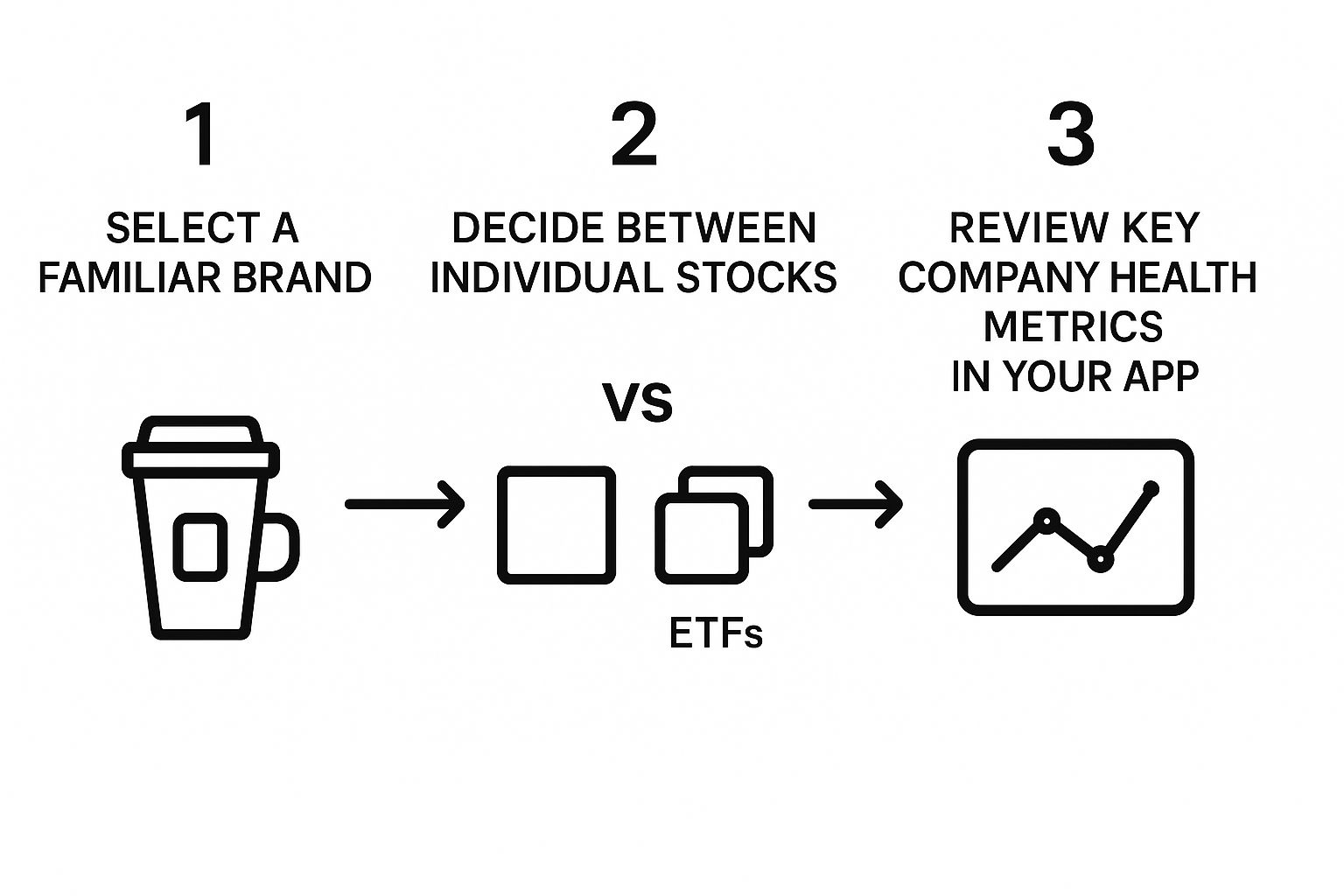
Individual Stocks vs. ETFs
As you start jotting down company ideas, you’ll hit a fork in the road: should you buy individual stocks or go for an Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF)?
An individual stock is exactly what it sounds like – a single slice of one company. An ETF is more like a curated playlist. It holds dozens or even hundreds of different stocks all at once. For example, an S&P 500 ETF lets you own a tiny piece of the 500 largest companies in the U.S. with a single click.
For new investors, ETFs are a fantastic way to instantly spread out your risk. If one company in the "playlist" has a bad month, it’s balanced out by all the others.
This simple infographic breaks down the selection process into a few clear steps.
As the visual shows, getting started can be as easy as picking a brand you trust and then deciding if you want just that one company or a more diversified basket. If you want to dive deeper into how these funds work, you can explore the key differences in our detailed guide on ETF vs mutual funds.
Whatever you pick, your brokerage app will have simple tools to do a quick "health check" on a company or fund before you commit your cash.
Making Your First Stock Purchase
You've done the work and picked your first stock. Now for the exciting part – actually buying it. Thankfully, this is way simpler than you might think.
Just open your brokerage app, search for the company's name or its ticker symbol (like NKE for Nike), and tap the "Trade" or "Buy" button. Easy.
From there, you just need to tell the app how you want to buy the stock. This is where you’ll see a couple of key terms called order types. Understanding these is the secret to placing your first trade with confidence.
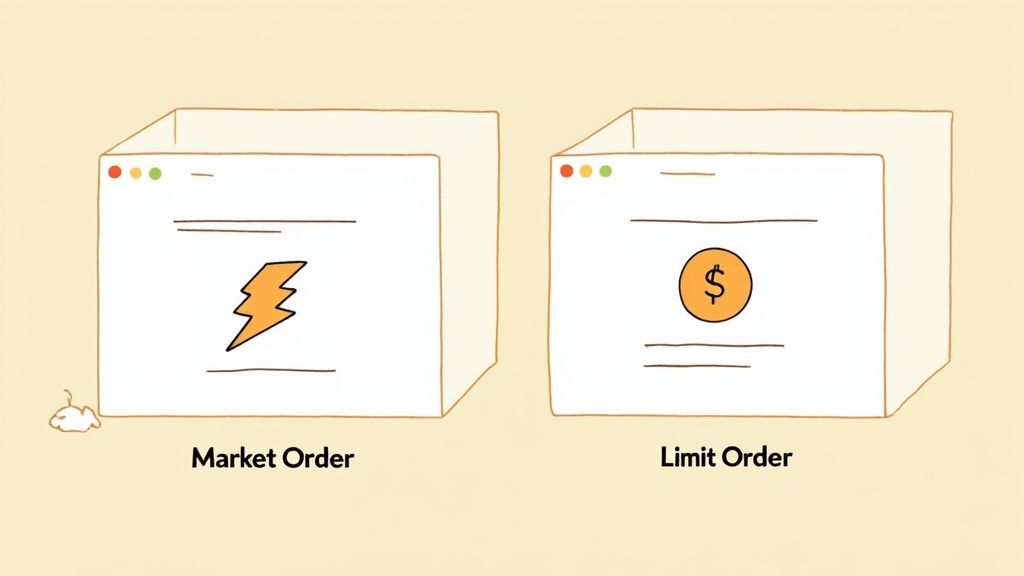
Market Orders vs. Limit Orders
The two main choices you'll see are market orders and limit orders.
A market order is the most straightforward option. It tells your broker, "I want to buy this stock right now, at whatever the current price is." It's fast, simple, and your order will almost always go through instantly. For most beginners, a market order is the perfect choice.
A limit order gives you more control. It's like saying, "I only want to buy this stock if the price drops to a specific number or lower." For instance, if Nike is trading at $95 a share, you could place a limit order for $94.50. Your purchase will only happen if the stock price hits your target. It's a great tool if you have a very specific price in mind.
The Magic of Fractional Shares
So, what happens when you want to own a piece of a powerhouse like Amazon, but a single share costs thousands of dollars? This is where fractional shares completely change the game for new investors.
Instead of needing the cash for a full share, you can just buy a small slice of one.
You don't need a huge bank account to get started. With fractional shares, you can buy $5 worth of Tesla or $10 worth of Apple. This lets you build a portfolio filled with amazing companies, even if you're starting small.
This is what makes modern investing so accessible. It allows you to begin your journey with whatever amount you're comfortable with. So go on, place that first order – you're officially an investor now.
Building Good Habits for Long Term Growth
Buying your first stock is a huge milestone, but let's be real: the secret to building actual wealth isn't about one lucky pick. It’s about building simple, repeatable habits you can stick with for years.
The real game is won with patience, not timing. Legendary investor Warren Buffett couldn't have said it better:
"The stock market is a device for transferring money from the impatient to the patient."
This mindset is your secret weapon. The market will have days where it feels like a rollercoaster. But history has shown us that the market trends upward over the long haul. Keeping your cool and sticking to your plan is how you come out on top.
Put Your Investing on Autopilot
One of the most powerful habits you can form is Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA). It sounds way more complicated than it is. All it means is investing a fixed amount of money on a regular schedule – say, $25 every Friday – no matter what the market is doing.
This simple strategy works like a charm:
- When prices drop, your $25 automatically buys more shares.
- When prices are up, that same $25 buys fewer shares.
This takes the emotion and guesswork out of investing. No more stressing about trying to "time the market." It’s a disciplined, set-it-and-forget-it method that builds wealth steadily. Even Ashton Kutcher, known for his acting, is a savvy tech investor who talks about the power of automating good financial habits.
Don't Put All Your Eggs in One Basket
Another key habit is diversification. Think of it this way: you wouldn't bet your entire life savings on a single roll of the dice, so why put all your money into just one company? Spreading your investments across different stocks and industries gives you a crucial safety net.
The numbers back this up. Over the past century, global stocks have delivered an average annual return of around 5-7% after inflation. An attention-grabbing fact is that this return is significantly higher than what you'd get from gold, bonds, or just holding cash. You capture this long-term growth by holding a mix of investments.
If you want to dive deeper into these historical trends, check out the UBS Global Investment Returns Yearbook.
When you combine patience with automation and diversification, you're not just investing – you're building a powerful system for long-term growth. These habits aren't flashy, but they are the bedrock of any successful investing journey.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Stepping into the world of investing can feel a bit like learning a new language. You're going to have questions, and that's not just normal – it's smart. Let's tackle some of the biggest ones right away.
Even the sharpest investors started at square one. They asked questions, learned the ropes, and made their moves. Your journey starts the same way.
How Much Money Do I Really Need to Start?
Honestly, you can probably start with the cash from your part-time job. Thanks to fractional shares, most modern brokerage apps let you get in the game with as little as $5.
The starting amount isn't nearly as important as the habit. It’s far more powerful to invest $25 every month than to wait until you have a "perfect" lump sum. Consistency is where the magic happens.
Is This Just a Nicer Word for Gambling?
Not if you’re doing it right. Gambling is pure chance, like betting on a coin flip. You have zero control.
Smart investing is about owning a piece of a real business. You're buying into a company that you believe has a solid plan to grow and succeed over time.
You can’t control a roll of the dice, but you can absolutely research a company, understand what it sells, and make an educated decision. While there's always risk, you minimize it by thinking like a business owner, not a high-roller in Vegas.
Stocks vs. ETFs: What’s the Difference?
Let’s use a food court analogy. Buying a single stock is like ordering just a slice of pizza. You’re betting everything on that one slice being delicious.
An ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund) is like getting the combo meal – the pizza, fries, and a drink all in one go.
The combo meal (the ETF) gives you instant variety. It holds dozens or even hundreds of different stocks. So, if the pizza company has a bad day, the fries and drink can help balance things out. For beginners, ETFs are an incredible tool for instant diversification.
How Often Should I Be Checking My Portfolio?
I know it's tempting. You put your money in, and you want to see what it's doing every five minutes. But this is usually a recipe for stress.
The market has daily mood swings – it zigs and zags constantly. For anyone investing for the long term, checking in once a month or even quarterly is plenty. Your goal is to let your money grow over years, not minutes.
Ready to put this knowledge into practice? At financeillustrated.com, we specialize in making the markets feel less intimidating and a lot more fun. Our free Trading School and interactive simulators are built to boost your confidence before you risk a single real dollar. Start your journey with us at https://financeillustrated.com.